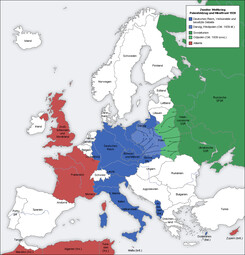
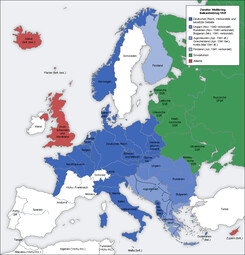
The complete course of World War II (1939–1945) 💥
Edumaps Wissen📑 Content Overview
-
- The Opponents
- Reasons and Victims
- Terms
- March 1938 – Germany annexes Austria
- Sep 1938 – Munich Agreement
- March 1939 – Annexation of Czechoslovakia
- ⚔️ Sep 1939 – Attack on Poland – Beginning of War
- Sep 1939 – Poland surrenders
- Sep 1939 to May 1940 – Phoney War
- April/May 1940 – Occupation of Denmark and Norway
- ⚔️ May/June 1940 – Attack on France (Blitzkrieg)
- May/June 1940 – British evacuation at Dunkirk (France)
- June 1940 – Italy enters the War
- June 1940 – Armistice with France
- June 1940 – Soviet Union occupies the Baltic States
- July to Oct 1940 – Battle of Britain
- Oct 1940 – Italy attacks Greece
- Nov 1940 – Hungary, Romania and Slovakia join the Axis powers
- Feb 1941 – Afrika Korps in North Africa
- April 1941 – Attack on Yugoslavia
- ⚔️ June 1941 - Attack on Russia (Eastern Front)
- Oct to Dec 1941 – Battle of Moscow – Soviet counteroffensive
- Dec 1941 – Attack by Japan at Pearl Harbor
- Dec 1941 – Declaration of war USA/GB on Japan
- Dec 1941 – Germany declares war on the USA
- May 1942 – Beginning of British bombing raids on Germany
- ⚔️ Jun to Sep 1942 – Advances on the Eastern Front
- ⚔️ Nov 1942 to Feb 1943 – Battle of Stalingrad (Turning Point in the War)
- May 1943 – German defeat in North Africa
- July 1943 – Operation Citadel (Battle of Kursk)
- July 1943 – Allies take Sicily
- Sep 1943 – Italy surrenders
- Nov 1943 – Soviet Union conquers Ukraine
- Jan to June 1944 – Italy is defeated
- ⚔️ June 1944 – Allied attack at Normandy (France)
- June 1944 – Soviet Union conquers Belarus
- Aug 1944 – Liberation of France
- Dec 1944 to Jan 1945 – Battle of the Bulge
- Jan 1945 - Major offensive by the Soviet Union
- April 1945 – Red Army in Berlin
- April 1945 – Suicide of Adolf Hitler
- May 1945 – Surrender of Germany
- Aug 1945 – Atomic Bombs and Surrender of Japan
Introduction
Reasons and Victims
-
The war was in many ways a continuation of the disputes of World War I (that took place from 1914 to 1918).
- The Peace Treaty of Versailles imposed conditions that damaged Germany's economy in the long term. The cession of areas and high reparation payments (compensation for damages).
-
The Second World War was the largest and most devastating war in our history. It is estimated that 50 to 70 million people died as a result of the war.
-
⚙ a02
Terms
-
- Germany was also called "German Reich".
- Russia was also called "Soviet Union".
- The German army was called "Wehrmacht".
- The Russian army was called "Red Army".
- "Annexion" means the takeover of a territory by another country. Mostly by military force (occupation).
-
⚙ a03
1938 (The Year before the War)
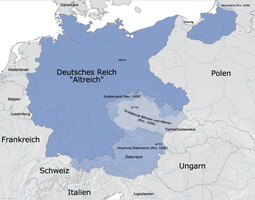
March 1938 – Germany annexes Austria
- Austria is solemnly incorporated into the German Reich on March 12, 1938.
- See also: Annexation of Austria (Anschluss)
-
⚙ a04
Sep 1938 – Munich Agreement
-
The "Munich Agreement" was a treaty between the German Empire, Great Britain, France and Italy.
-
The agreement of September 29, 1938 stipulated that Czechoslovakia had to cede the Sudetenland (which belonged to Germany before the First World War) to the German Reich within ten days.
- See also: Munich Agreement
-
⚙ a05
1939 (Beginning of War)
March 1939 – Annexation of Czechoslovakia
-
The Wehrmacht invaded Czechoslovakia in March 1939. The country is annexed by Germany.
- See also: Occupation of Czechoslovakia (1938–1945)
-
⚙ a06
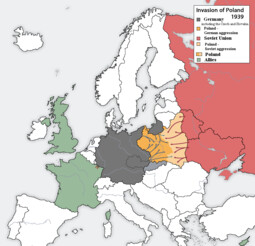
⚔️ Sep 1939 – Attack on Poland – Beginning of War
-
On September 1, 1939, the Wehrmacht attacks Poland.
-
This is the beginning of World War II.
-
In response, on September 3, 1939, France and Great Britain declared war on Germany.
-
On September 17, 1939, the Soviet Union also attacks Poland from the east.
- See also Invasion of Poland
-
⚙ a07
Sep 1939 – Poland surrenders
-
On September 27, 1939, Warsaw was taken by the Wehrmacht.
-
Poland is defeated and under German control.
- See also Siege of Warsaw (1939)
-
⚙ a08
Sep 1939 to May 1940 – Phoney War
-
Despite France and Great Britain declaring war on Germany in September 1939, there are no military conflicts between the countries in 1939.
-
The western front remains largely passive. This period is known as the "Phoney War".
- See also Phoney War
-
⚙ a09
1940
April/May 1940 – Occupation of Denmark and Norway
-
On April 9, 1940, the Wehrmacht invades Denmark and Norway, ending the Phoney War.
-
Denmark surrenders on the day of the attack. Norway surrendered on June 9, 1940.
- See also Operation Weserübung
-
⚙ a10
⚔️ May/June 1940 – Attack on France (Blitzkrieg)
-
On May 10, 1940, the Wehrmacht attacks France and also took over the neutral countries of Belgium, the Netherlands and Luxembourg.
-
The Wehrmacht offensive runs until June 25, 1940 and is a particular military success, as the French army is considered to be extremely strong at this time.
- The campaign is called „Blitzkrieg“ because it is focused on one area and because of the speed and concentrated military force.
- See also Battle of France
-
⚙ a11
May/June 1940 – British evacuation at Dunkirk (France)
-
The Wehrmacht advances further into French territory and puts the British troops (that are stationed there) under pressure.
-
From May 26 to June 4, 1940, the British army (trapped in France) is evacuated by boat from Dunkirk to England.
- See also Dunkirk evacuation
-
⚙ a12
June 1940 – Italy enters the War
-
On June 10, 1940, Italy declared war on France and Great Britain.
-
Italy entered the war as an ally of Germany.
-
The Italian army attacks the south of France on the same day, but without success.
- See also Italy's declaration of war on France and Great Britain and Italian invasion of France
-
⚙ a13
June 1940 – Armistice with France
-
On June 14, 1940, the Wehrmacht takes the French capital Paris.
-
On June 22, 1940, France signed an armistice agreement with Germany.
-
With the agreement, Germany will receive the northern half of France and the entire Atlantic coast.
-
The south of France becomes the state of "Vichy France" which collaborates with Germany.
- See also Vichy France
-
⚙ a14
June 1940 – Soviet Union occupies the Baltic States
-
On June 14, 1940, the Soviet Union occupies the Baltic states of Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania.
-
The countries are annexed as Soviet republics (3 - 6 August 1940).
- See also Occupation of the Baltic states
-
⚙ a15
July to Oct 1940 – Battle of Britain
-
The Battle of Britain takes place from July 10th to October 31st, 1940.
-
The German Luftwaffe attempts to force a surrender by attacking Britain. The operation becomes a failure.
- See also Battle of Britain
-
⚙ a16
Oct 1940 – Italy attacks Greece
-
On October 28, 1940, Italy attacks Greece from the territory of Albania.
-
The Greek-Italian war ended on April 23, 1941, through the intervention of the Wehrmacht and results in the capitulation of Greece.
- See also Greco-Italian War
-
⚙ a17
1941
Feb 1941 – Afrika Korps in North Africa
-
In February 1941, Germany sends the "Afrika Korps" to North Africa to support the Italian army in the attack on Egypt.
-
The operation ran from February 21, 1941 to June 30, 1943 and ended in a defeat for the Wehrmacht.
- See also Afrika Korps
-
-
⚙ a19
April 1941 – Attack on Yugoslavia
-
On April 6, 1941, Germany, Italy and Hungary attack the Kingdom of Yugoslavia.
-
In addition, the Wehrmacht is now fighting against Greece.
-
On April 17, 1941, Yugoslavia surrenders.
-
On April 23, 1941, Greece surrenders.
- See also Balkans campaign (World War II)
-
⚙ a20
⚔️ June 1941 - Attack on Russia (Eastern Front)
-
On June 22, 1941, Germany attacks the Soviet Union (Operation Barbarossa).
-
The German-Soviet War begins.
- From June to November 1941, the Wehrmacht drives the Red Army out of the Baltic states. See Baltic offensive.
- On September 8, 1941, the siege of the Russian city of Leningrad (St. Petersburg) begins. It lasts until January 27, 1944. See Siege of Leningrad.
- In the south, the Wehrmacht captures Kyiv (Ukraine) in September 1941 and in November 1941 the Russian city of Rostov-on-Don.
- See also Operation Barbarossa and Eastern Front (World War II)
-
⚙ a21
Oct to Dec 1941 – Battle of Moscow – Soviet counteroffensive
-
From October 2, 1941, the battle for Moscow begins.
- By the end of November 1941, the Wehrmacht manages to advance up to 35 km to the Russian capital Moscow.
-
On December 6, 1941, however, a powerful Soviet counter-offensive drives the Wehrmacht into a chaotic retreat.
- See also Battle of Moscow
-
⚙ a22
Dec 1941 – Attack by Japan at Pearl Harbor
- December 7, 1941 Japan attacks USA at Pearl Harbor (Hawaii).
- See also Attack on Pearl Harbor
-
⚙ a23
Dec 1941 – Declaration of war USA/GB on Japan
-
On December 8, 1941, the United States and Great Britain declared war on Japan.
- The Pacific War, which has been raging between China and Japan since 1937, intensified with the entry of the USA and Great Britain.
-
⚙ a24
Dec 1941 – Germany declares war on the USA
-
On December 11, 1941, Germany and Italy, Japan's allies, declare war on the USA.
- See also German declaration of war against the United States
-
⚙ a25
1942
May 1942 – Beginning of British bombing raids on Germany
-
On May 30, 1942, the British bomb Cologne for the first time.
-
The bombing brought the war to German territory and lasted until the end of the war in May 1945.
-
Many German cities are attacked.
- In particular, the air raids on Dresden in February 1945 destroyed most of the city.
-
⚙ a26
⚔️ Jun to Sep 1942 – Advances on the Eastern Front
-
On June 28, 1942, the Wehrmacht (with allied troops) launched a new offensive against the Soviet Union.
- German troops invade Stalingrad (Volgograd) on the Volga until mid-September 1942. In addition, the Crimean peninsula is secured.
-
⚙ a27
⚔️ Nov 1942 to Feb 1943 – Battle of Stalingrad (Turning Point in the War)
- On November 23, 1942, Soviet troops counterattacked in Stalingrad (Volgograd). The Red Army breaks through and traps the German army in the city.
-
Since Hitler forbids the German army from surrendering, it endures another two months without supplies and finally capitulates on February 2, 1943.
-
This victory of the Red Army against the Wehrmacht is considered a turning point in the war.
- See also Battle of Stalingrad
-
⚙ a28
1943
May 1943 – German defeat in North Africa
- Already on October 23, 1942, British troops defeated the Germans and Italians at El Alamein in Egypt. This was followed by a retreat to Libya.
- On November 8, 1942, American and British troops land in Algeria and Morocco. The troops quickly advance to the western border of Tunisia.
-
Finally, on May 12, 1943, the German and Italian troops in North Africa are defeated by the Allies. They capitulate on May 13, 1943 in Tunisia.
-
⚙ a29
July 1943 – Operation Citadel (Battle of Kursk)
- The Wehrmacht launches an attack on the Soviet salient around the Russian city of Kursk.
-
This attack is considered the last major offensive against the Soviet Union.
- See also Operation Citadel and Battle of Kursk
-
⚙ a30
July 1943 – Allies take Sicily
- On July 10, 1943, British and American troops land on Sicily (Italy) and take the island.
-
Sicily is defeated in August 1943.
-
⚙ a31
Nov 1943 – Soviet Union conquers Ukraine
-
The Red Army continues to drive back the Wehrmacht from the Soviet Union.
- On November 6, 1943, Soviet troops took the Ukrainian city of Kyiv.
-
⚙ a33
1944
Jan to June 1944 – Italy is defeated
- On January 22, 1944 Allied troops land near Anzio, south of Rome and fight against the Italian troops.
-
See also Battle of Anzio
-
On June 5, 1944, the Allies take Rome.
-
Italy is defeated.
-
⚙ a34
⚔️ June 1944 – Allied attack at Normandy (France)
- On June 6, 1944, the Allies attack the German positions at the Normandy (France).
- The day of the attack is known as "D-Day". In just one day there were heavy casualties on both sides.
- See also Normandy landings
-
Now Germany is in a war on two fronts (Western Front and Eastern Front).
-
⚙ a35
June 1944 – Soviet Union conquers Belarus
- On June 22, 1944, the Red Army launches a massive offensive in eastern Belarus and destroyes the German Army Group.
- By August 1, 1944, the Red Army advances to the Vistula River and then continues to advance to Warsaw (Poland).
-
⚙ a36
Aug 1944 – Liberation of France
-
On July 25, 1944, Allied troops break out of Normandy and advance towards Paris.
- On August 15, 1944, Allied forces land at Nice (southern France) and advance rapidly northeast towards the Rhine.
-
Finally, on August 25, 1944, Paris is liberated by the Allies.
-
By December 1944 practically all of France, most of Belgium and part of the southern Netherlands have been liberated.
-
⚙ a37
Dec 1944 to Jan 1945 – Battle of the Bulge
- On December 16, 1944, the Wehrmacht launches a final counter-offensive and attempts to occupy the port of Antwerp (Belgium) and thereby split the Allied forces along the German border.
-
The attempt fails. From January 1, 1945, the Wehrmacht is in retreat.
- See also Battle of the Bulge
-
⚙ a38
1945
Jan 1945 - Major offensive by the Soviet Union
-
On January 12, 1945, the Soviet Union's major offensive begins.
- The Red Army conquers Warsaw and Kraków (Poland) in January 1945.
- Budapest (Hungary) is conquered by the Red Army on February 13, 1945, after a two-month siege.
-
⚙ a39
April 1945 – Red Army in Berlin
- In April 1945 the Red Army reaches the German capital Berlin.
- See also Battle of Berlin
- On April 13, 1945, the Red Army also takes Vienna (Austria) ein.
-
⚙ a40
April 1945 – Suicide of Adolf Hitler
-
On April 30, 1945, Adolf Hitler kills himself.
-
⚙ a41
May 1945 – Surrender of Germany
-
On May 7, 1945, Germany surrendered unconditionally.
-
The unconditional surrender of Germany is formally announced on May 8, 1945.
-
The fighting in Europe is over. This ended the Second World War in Europe.
- See also German Instrument of Surrender
-
⚙ a42
Aug 1945 – Atomic Bombs and Surrender of Japan
-
On August 6, 1945, the USA dropped the first atomic bomb on Hiroshima (Japan).
-
On August 9, 1945, the second atomic bomb is dropped by the USA on Nagasaki (Japan).
-
On August 14, 1945, Japan surrendered unconditionally.
-
The unconditional surrender of Japan is completed on September 2, 1945.
-
This is considered the end of World War II.
- See also Surrender of Japan
-
⚙ a43